Avascular Necrosis Treatment
Avascular Necrosis Treatment
+25
Patients suffering from Avascular Necrosis healed.
1
Clinical trial on Avascular Necrosis. The world’s only scientific evidence.
+25 |
1 |
Patients suffering from Avascular Necrosis healed.
Clinical trial on Avascular Necrosis. The world’s only scientific evidence.

Patients

Clinical Trials (Largest scientific evidence worldwide)

Doses of Cultured Mesenchymal Stem Cells

Endorsed by Health Authorities
Mariona Borrell: "I couldn't walk more than 10 minutes straight without sitting down."
Mariona Borrell: "I couldn't walk more than 10 minutes straight without sitting down."
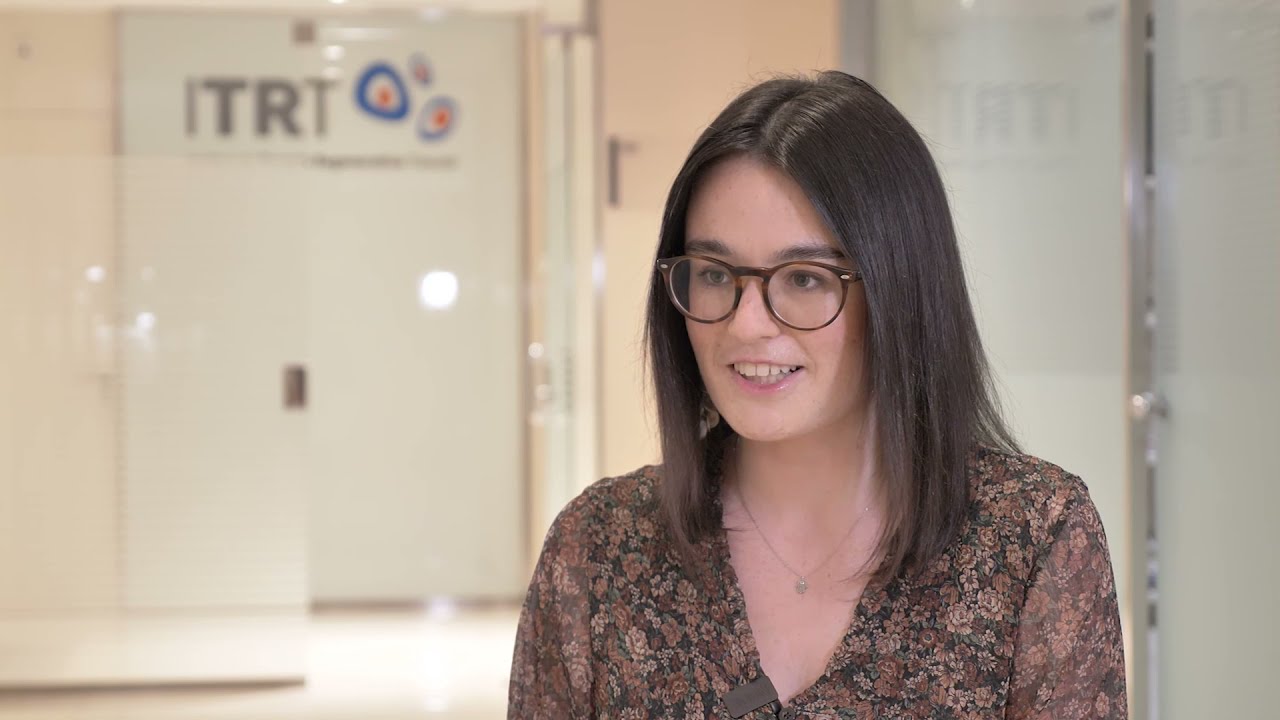

After treating her with 40 Million Cultured Stem Cells, she has gone from not being able to walk more than 10 minutes, living with pain and looking with concern to the future, to enjoy a full life, with quality and confidence in the future.
She found a definitive solution, minimally invasive and without the need for prostheses.
Mariona Borrell: "I couldn't walk more than 10 minutes straight without sitting down."
After treating her with 40 Million Cultured Stem Cells, she has gone from not being able to walk more than 10 minutes, living with pain and looking with concern to the future, to enjoy a full life, with quality and confidence in the future.
She found a definitive solution, minimally invasive and without the need for prostheses.

What is Avascular Necrosis?
Avascular necrosis (AVN) is the death of bone tissue due to a loss of blood supply. You might also hear it called osteonecrosis, aseptic necrosis, or ischemic bone necrosis.
If untreated, it can cause the bone to collapse. It most commonly affects the hip, but may also occur in shoulders, knees and ankles.
In its early stages, AVN usually has no symptoms. As the disease grows worse, it becomes painful. At first, pain may only arise if the affected bone is under pressure, but later it can become constant.
Collapse of the bone and surrounding joint can cause severe pain and inability to use the joint. The time that elapses between the initial symptoms and bone collapse can range from several months to more than a year.
What is
Avascular Necrosis?
Avascular Necrosis (AVN) is the death of bone tissue due to a loss of blood supply. You might also hear it called osteonecrosis, aseptic necrosis, or ischemic bone necrosis.
If untreated, it can cause the bone to collapse. It most commonly affects the hip, but may also occur in shoulders, knees and ankles.
In its early stages, AVN usually has no symptoms. As the disease grows worse, it becomes painful. At first, pain may only arise if the affected bone is under pressure, but later it can become constant.
Collapse of the bone and surrounding joint can cause severe pain and inability to use the joint. The time that elapses between the initial symptoms and bone collapse can range from several months to more than a year.
Avascular Necrosis from Femoral head (hip)
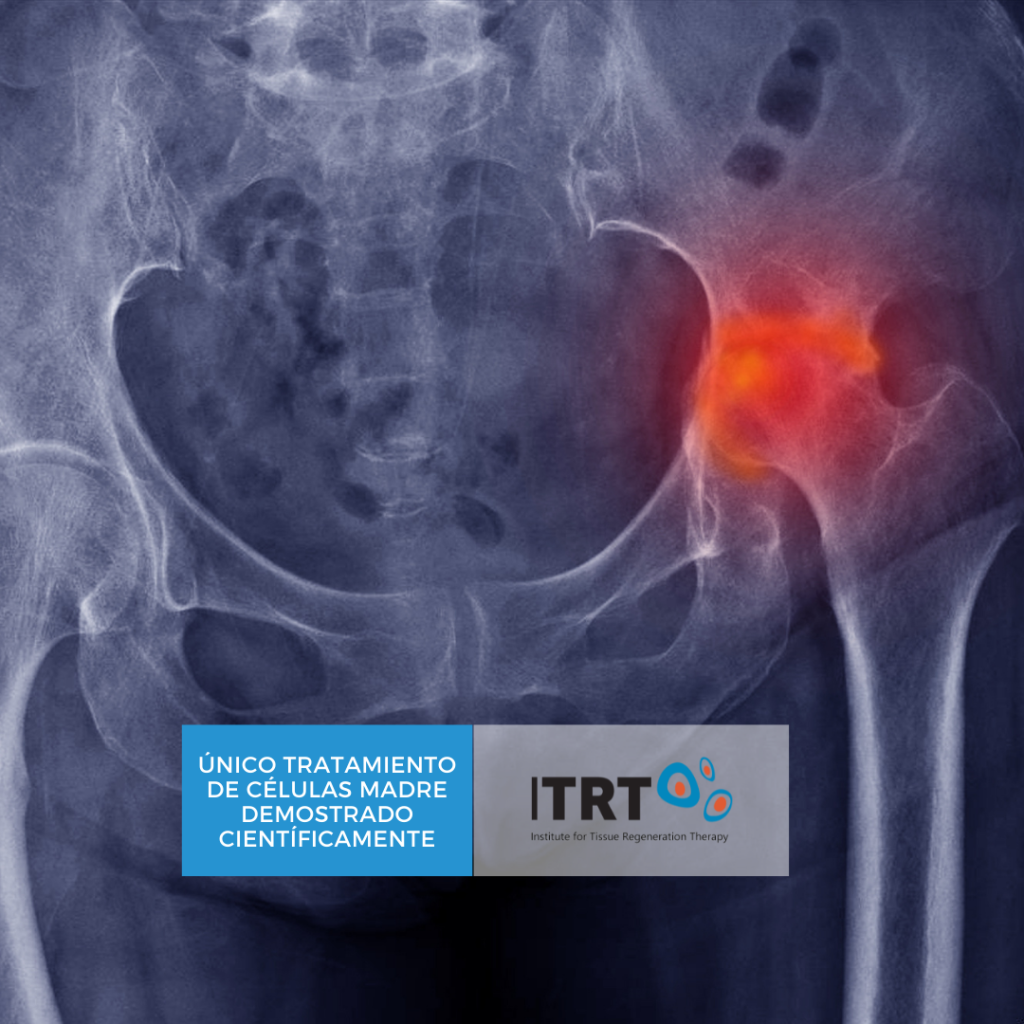
It can occur due to a variety of either traumatic or atraumatic causes that include fractures, dislocations, chronic steroid use, alcohol, coagulopathy, and may have congenital and many other causes. Only in the States, are reported from 10.000 to 20.000 new cases per year.
If untreated, the disorder can progress and require prosthesis implantation in most patients. At ITRT, we offer a definitive, permanent solution that prevents to implant expensive and annoying prosthesis.
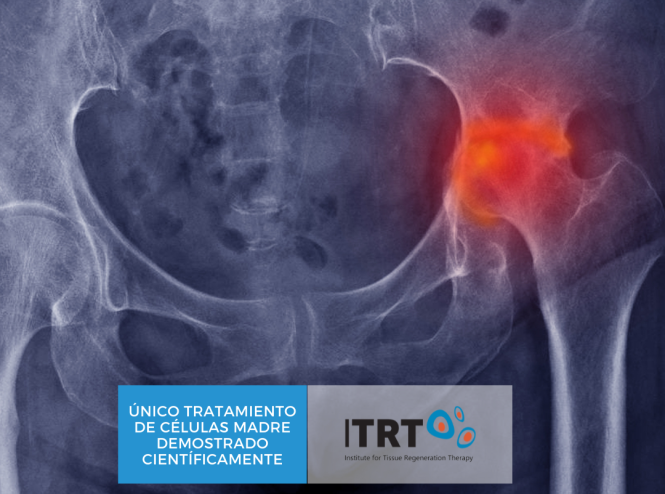
Avascular Necrosis from
Femoral head (hip)
It can occur due to a variety of either traumatic or atraumatic causes that include fractures, dislocations, chronic steroid use, chronic alcohol use, coagulopathy, and may have congenital and many other causes. Only in the States, are reported from 10.000 to 20.000 new cases per year.
If untreated, the disorder can progress and require prosthesis implantation in most patients. At ITRT, we offer a definitive, permanent solution that prevents to implant a prosthesis.
Why our exclusive treatment is one-of-a-kind?
Not all stem cell treatments are equal; many of them barely contain a handful of stem cells, at best.
Our exclusive therapy of cultivated stem cells is the only one in the field of Regenerative Medicine that has scientifically demonstrated its effectiveness and safety. Only ITRT applies this therapy, which is the result of over 20 years of research.
Differences of our exclusive therapy from the rest of the mislabeled ‘stem cell’ treatment:
Dosage:
We have scientifically demonstrated in clinical trial that only by using millions of units can the regeneration process be activated. Our therapy applies millions of stem cells, certified by our laboratory.
Clinical trials:
Over the course of more than 20 years, we have conducted 23 clinical trials that have demonstrated the efficacy and safety of our therapy, constituting the largest knowledge base worldwide in regenerative therapy.
Tipology:
There are many types of stem cells, but we have demonstrated that only 3 of them are effective when applied to tissues. In the laboratory, we select the correct types of stem cells to ensure regeneration.
Cellular activation:
Once the appropriate stem cells are selected, the very small quantity obtained through isolation undergoes an activation process, causing them to begin multiplying until reaching millions of units.

Cells from donors:
We have demonstrated in several clinical trials that we can use stem cells from other donors. This fact is very important especially for elderly patients, those with urgent needs, or serious illnesses.
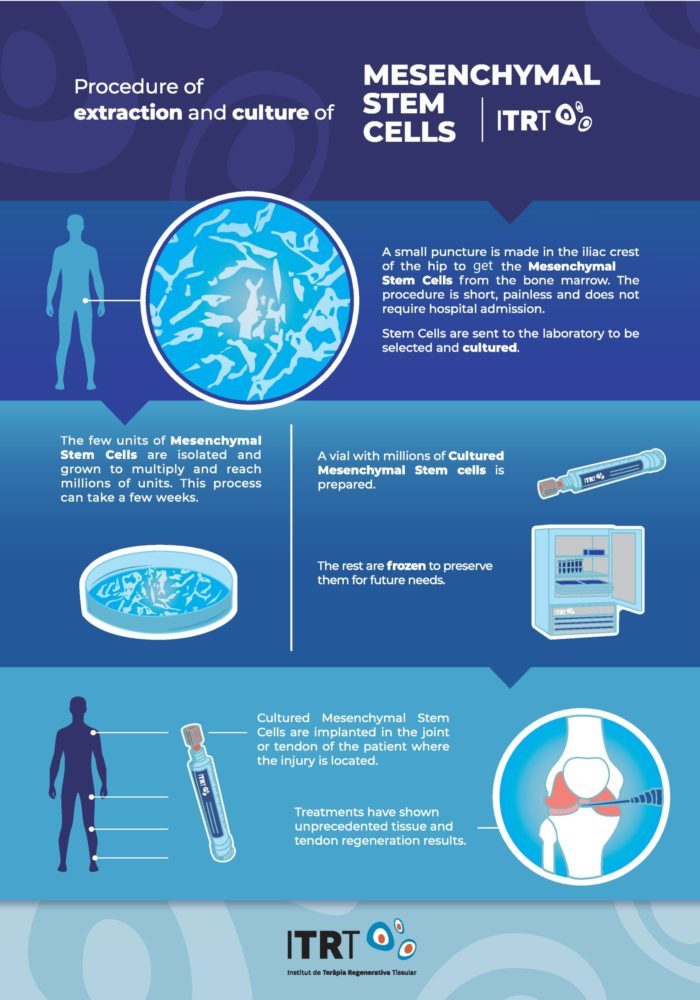
The ultimate treatment for AVN from Femoral Head: Cultured Stem Cells
The cell therapy that we perform at ITRT consists of creating a tunnel in the bone to implant 80 Million of Cultured Stem Cells in the hip. ITRT treatment has been shown to prevent joint collapse and the need to implant a prosthesis.
This treatment can only be performed in cases in which the femoral head still retains its spherical anatomical shape.
Cultured Mesenchymal Stem Cell therapy practiced by our medical team is performed within strict compliance of the EMAA and AEMPS regulatory framework and all patients are included in a clinical trial supervised by the Clinical Research Ethics Committee and EMAA.
Scientific Endorsement
Tell us about your case, we can help you
Regenerate bone and cartilage
Make prosthesis unnecessary
Avoid hip replacement